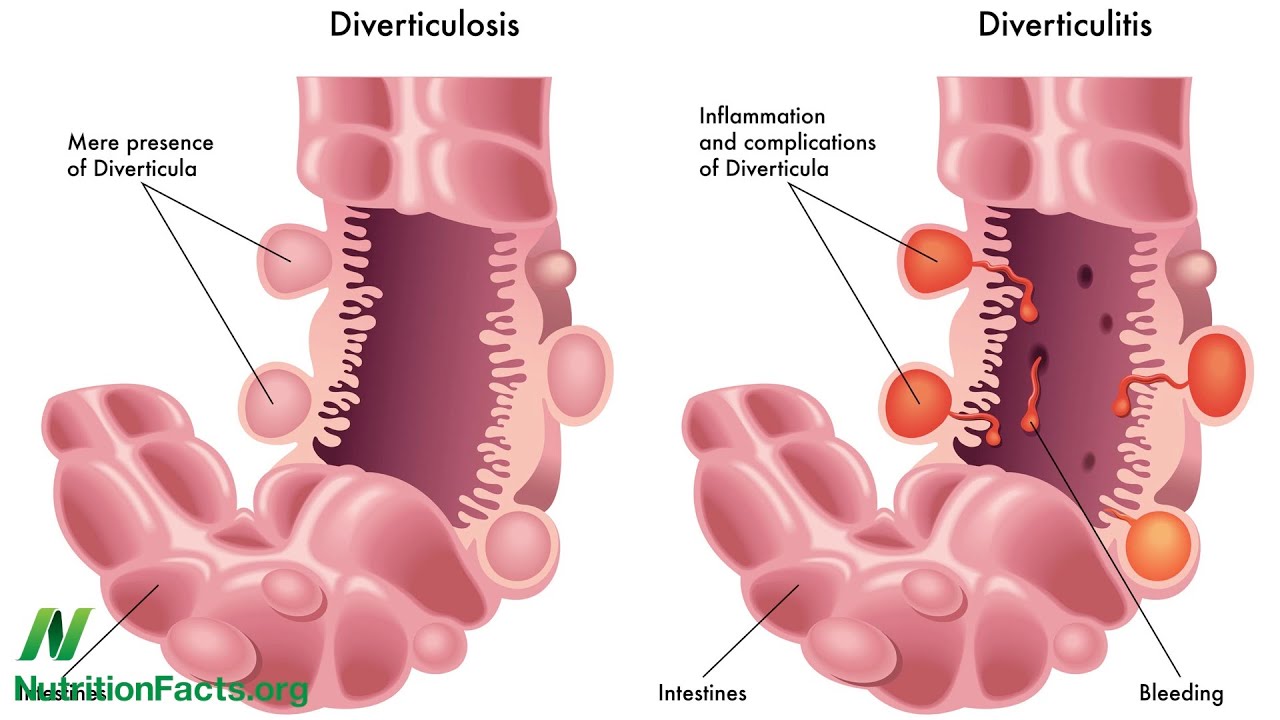
When diagnosing diverticulitis, the first thing that doctors usually do is carry out a blood test followed by other tests such as CT scans, X-rays and even ultrasounds.

Full Blood Count
The full blood count can tell doctors a lot about your current health. The number of red blood cells can tell doctors if you’re anaemic and perhaps losing blood. But one of the most important markers in a blood test when trying to check for diverticulitis is the white blood cell count.
White blood cells are a part of the immune system and are responsible for fighting diseases and illnesses. When a pathogen (harmful bacteria or virus) enters the body, it is identified by the immune system which then increases the number of white blood cells. An amount of white blood cells higher than the normal range could be considered to be a sign of infection. However, it is possible to have diverticulitis but not have a measurable increase in white blood cells. So a normal blood result doesn’t necessarily mean that you don’t have an infection or inflammation in the bowel.
CRP (C-Reative Protein)
CRP is known as an inflammation marker – it is a protein released by human tissues when they are inflamed. The higher the amount of CRP in the blood, the more inflammation there is. Having elevated CRP in addition to abdominal pain and other symptoms is a good indicator of diverticulitis. However, your doctor should also check carry out an abdominal examination too just in case the inflammation is coming from somewhere else.

Abdominal Examination
It’s likely your doctor may carry our an abdominal examination. This is where the doctor will press on your abdomen to discover where the pain originates and if it is the bowel that is inflamed. It’s important to be very honest about the pain you are feeling at this point so that the doctor can rules out any other issues or sources of inflammation.
CT scan
This is usually the most effective way to diagnose diverticulitis. A CT scan can be done with or without contrast, but contrast certainly helps when interpreting the results. The two main types of contrast are oral and intravenous (IV). The oral contrast is often a liquid mixed with water that you drink before the scan. It helps to highlight the digestive tract on your scan. The IV contrast is injected into a vein and reaches the tissues and helps them show up better on the scan. Some hospitals may choose to have their patients take both types of contrast. However, it is important than you let the doctor know of any allergies you have before you receive any contrast agents.
A CT scan is painless and just requires the patient to hold their breath for short periods. Let the technician or doctor performing the scan know if you suffer from asthma or COPD or any problem that makes you find it difficult to hold your breath.
After the scan, your results will not be ready immediately since they will need to be looked at by a doctor and a thorough report written. See my post on CT scans for more information.
X-rays
Some doctors may choose to send their patients for X-rays. This is to check for perforations in the bowel since X-rays can easily pick up excess gas in the abdomen that may be leaking out from the bowel. The results of an X-ray are much more immediate which is why this test might be chosen particularly if the patient is in a lot of pain or has a history of perforations and sepsis.
Ultrasound
Again, some doctors may want to send their patients for an ultrasound. This is very common during first time diagnoses when patients are doctors don’t know that the patient even has diverticular disease yet. An ultrasound may also show an abscess or cyst as a result of diverticulitis. It may also be able to detect excess air of material in the abdomen. However, it is not as clear as a CT scan, but the results are more immediate.

Why don’t doctors use colonoscopies to diagnose diverticulitis?
It’s very rare that a doctor would use a colonoscopy to diagnose diverticulitis because while a patient has an infection, it would be very painful and a little dangerous to insert an endoscope. There is a chance that the colonoscopy during an infection could make it even worse or could even cause damage to the colon.
Have you been diagnosed with diverticulitis? Which methods did the doctors use to diagnose you?