It’s that time of the year again when you gather with friends and family to celebrate thanksgiving. Maybe you can’t wait to get stuck into your thanksgiving feast or perhaps the idea of it fills you with dread. Read our 7 tips for surviving Thanksgiving with a digestive disorder.
- Don’t over-eat! – Stick to small portions. Eating large portions puts you at risk of stomach ache, nausea, bloating, indigestion and cramps.
- Don’t eat too quickly – It may be the most delicious meal you’ll eat all year, but that’s all the more reason to savor each bite. Enjoy it! Take small bites and chew them well before swallowing. This will also help you to not over eat.
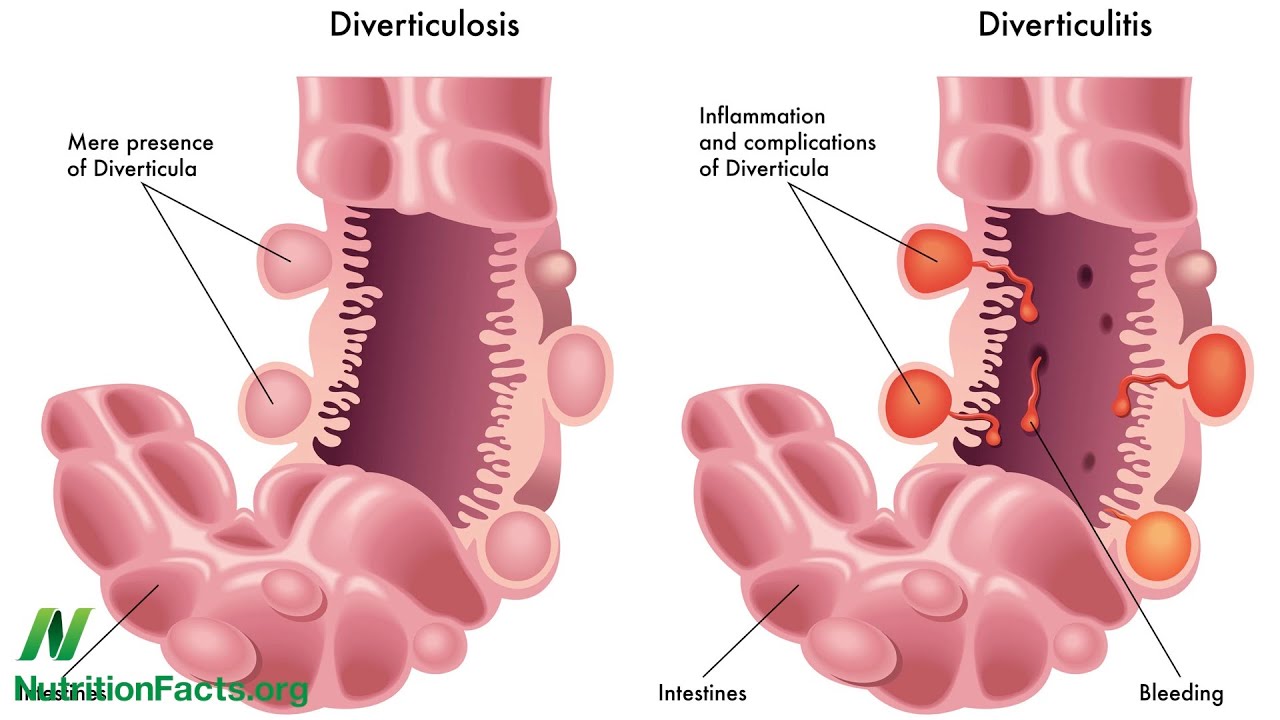
- Stay hydrated – you may be wanting to enjoy an extra large glass of wine with dinner or even rustle up an early egg nog, but remember, your body needs water to work at it’s best and keep you hydrated. Alcohol has a diuretic effect which means it causes your body to lose water. That’s why if you’re having an alcoholic drink this Thanksgiving, be sure to drink some extra water. Not to mention that a well hydrated bowel works better meaning a lower chance of constipation or of developing infections such as diverticulitis.
- If you get pain – switch to clear liquids only right away. It’s not worth taking chances. Pains are your body’s way of warning you that something isn’t right. Let your bowel and stomach rest by not giving them any more food.
- Be prepared – Make sure you are stocked up on any medicines or products you use to ease your digestive disorder or the symptoms it causes. You don’t want to have to rush out on Thanksgiving to find somewhere to find your favourite antacid. If you’re dining at someone else’s place, take everything you need to feel comfortable. You can even make yourself a little emergency pack with some essentials: For example; any medications you usually take for your stomach e.g. for reflux, cramps etc., painkillers, wet wipes, spare underwear if needed, etc.
- Avoid very fatty or rich foods – don’t go overboard with your helping of mac n cheese or your dollop of cream on your slice of pie. Also, go easy on the candied yams and glazed carrots. These foods can cause indigestion, acid reflux, nausea, IBS symptoms, diarrhea and problems if you have gallstones or have had your gallbladder removed. You can reduce fat in your meal by taking the skin off your turkey and only eating the light meat. Another idea is to only use a small amount of gravy on your food.
- Keep it simple: – Only eat foods you know you are usually okay with. It may be tempting to fill up on candied yams, but will it be worth it tomorrow when you’re doubled over in pain or stuck in the bathroom all day? One suggestion is: A small plate with some roast turkey (light meat), some potatoes a little gravy and a small piece of cornbread. But remember, we are all different. What you can eat without a problem, may cause someone else a lot of pain and discomfort. You can choose foods that are safe for you and just eat a little amount. Remember: while green beans and sprouts may seem like a healthy addition to your meal, it’s best not to risk it if you haven’t eaten these foods recently or you’re recovering from diverticulitis, a flare up of IBS, Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
By following this simple tips, you can avoid digestive problems and concentrate on celebrating with your loved ones. What are your plans for Thanksgiving this year and what do you plan to eat? Let me know in the comments.
Support the author and buy her a coffee by making a donation here: paypal.me/haylaki